Role of Python Libraries in Image Processing
October 30, 2025
Home >> Cloud Computing >> The Pros and Cons of Cloud Computing for Healthcare

Quick Summary
The growth and evolution of cloud computing for healthcare have made significant headway, transforming everything from maintaining patient records to enabling remote consultations with doctors across distances. This adoption of cloud healthcare computing has been increasing as institutes have sought in their pursuit of wielding the benefits of it while navigating its challenges. Here in this detailed blog, we are going to discuss both pros and cons of cloud computing within the healthcare industry, examine real-life case studies, and bring best practices into discussion for maximising its effectiveness.
Healthcare cloud computing is the process of exploiting distant servers to store, handle, and process healthcare data. Its basis does not lie in the classical model of where data is stored on a physical server or within the healthcare provider’s local computer at the hospitals and clinics. Instead, cloud healthcare solutions allow healthcare service providers access to all the vital data through the internet, thereby making the health data more accessible and flexible.
Cloud computing in healthcare industry is applied in a number of ways, such as storing Electronic Health Records (EHR), managing large volumes of imaging data, enabling platforms for telemedicine, and being the foundation for advanced analytics and AI-powered healthcare applications. It is fueled by better data management and the improvement of patient care alongside efficiency in operations.
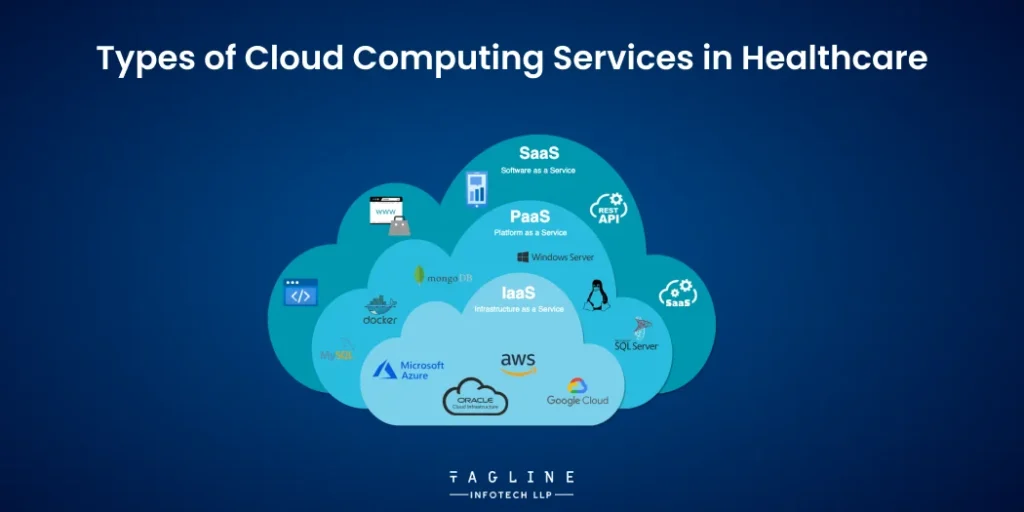
When healthcare organisations choose cloud computing, they commonly opt for one of the three types of services.
All the services above have their own advantages and practice within healthcare depending on what an organisation actually needs.
That cloud computing can be credited with the rise of healthcare is also partly due to its potential in revolutionising access, collaboration, and efficiency. Cloud healthcare computing allows for the easy storage and retrieval of great amounts of patient information in hospitals, clinics, or even individual practitioners. This is important in better patient results: healthcare professionals can obtain medical histories, lab results, and diagnostic images promptly, even remotely.
One of the key benefits of cloud managed services in healthcare is cost-effectiveness. Management of the physical server and data centres becomes expensive and time-consuming. Cloud service providers offer them to free the healthcare provider from the job for more care and less time on IT.
Cloud healthcare computing has a lot of advantages to the healthcare arena, from cost-effectiveness to enhanced patient care. Let’s take some of them:
Cost Efficiency: The most important aspect of cloud health computing is the cost-effectiveness. It saves healthcare organizations from making front-end investment in order to buy and maintain servers. Instead, they can use the subscription basis model where only utilized storages and services are paid while permitting maximum flexibility in using their finances.
Scalability: Storage and computing resources can quickly scale up or down for health institutions as they may need. It is because, in health institutions, the volume of data is exponentially growing as the digital health records, medical imaging, and other healthcare data increase in volume.
The cloud healthcare solution can help bridge the collaboration gap between health practitioners. Patient data will be shareable, in an instant, anywhere in the world, between doctors and specialists and other care providers as well. This gives a more holistic and coordinated way towards the healing of a patient, ultimately improving outcomes.
Accessibility and Mobility: Cloud computing provides doctors access to patient data at any time and from anywhere with an internet connection. This is particularly useful for healthcare providers in telemedicine and remote patient monitoring, wherein health care providers may need access to data real-time in virtual consultations.
Disaster Recovery and Backup: Providers in the cloud automatically perform backups and offer disaster recovery services to ensure there are no losses of critical data in case of server crash or a natural disaster. Disasters are a high sensitivity area for health care in regards to such risks because data integrity is necessary to safeguard patient safety and their treatments’ continuation.
Improved Security: Cloud computing vendors offer more robust levels of security, including encryption and multi-factor authentication, to secure sensitive health information. In theory, the duty of protecting the data vests with the healthcare provider as well as the vendor offering cloud computing. However, most of the cloud vendors are subject to stricter regulatory requirements including HIPAA compliance.
While cloud healthcare solutions offer many advantages, they come with several challenges that healthcare organizations must heed:
Data Security and Privacy Concerns: The biggest challenge in adopting cloud healthcare computing is ensuring data security. Healthcare data is highly sensitive, and a breach of data could lead to such serious legal and financial repercussions for institutions involved. Therefore, it is crucial for the institutions concerned to be very alert in choosing the right cloud provider who has a high level of security to ensure all patient data.
Compliance Issues: The healthcare industry is strictly regulated in the United States and throughout the rest of the world with HIPAA dictating how patient information must be handled. Ensuring the vendors using cloud are HIPAA compliant is difficult, and non-compliance may result in sizeable fines.
Service Outages: Cloud computing relies on internet connectivity. Where there is a service outage, access to patient data will be affected as much as no internet means the treating physician cannot access patient records for any suitable treatment or operations.
Lack of Control of Data: Since providers entrust external third-party cloud providers with their data, they lose some control over their data. Some institutions are uncomfortable allowing third-party vendors to handle and keep sensitive patient information safe.
Hidden Costs: Although the initial cost of the cloud is much reduced, monitoring has to be done on usage and service fees. Cloud services will be expensive, especially if storage and computation costs are not monitored, and their health record counts are not kept track by the healthcare institution.
Best practices to make the best of cloud healthcare solutions by both data security and good operational efficiency:
Select HIPAA Compliance Cloud Provider: Select one that is HIPAA compliant for his protection of patients’ data. Ensure the cloud provider follows the industry-specific standards as in the case of HIPAA in the U.S. or GDPR in the EU.
Encrypt Data: Patient data should be encrypted both in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorized access.
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Make multi-factor authentication for all access to the cloud-based systems to significantly reduce the risk of unauthorised access
Security Audits: Frequently assess and audit your cloud provider’s security practice to keep up to date with highest standard.
Create a Disaster Recovery Plan: Work with your cloud provider to establish a detailed disaster recovery plan so that you can regain your services as quickly as possible in the event of an outage or breach.
At Tagline Infotech, cloud computing in healthcare provides significant advantages, from cost savings and scalability to improved collaboration among healthcare teams. However, healthcare organizations must carefully address potential challenges such as data security, regulatory compliance, and downtime risks. By implementing best practices and partnering with reliable cloud service providers, healthcare institutions can unlock the full potential of cloud-based healthcare solutions, enhancing patient care, boosting operational efficiency, and ensuring robust business continuity.
Healthcare is being shifted to the cloud to scale up scalability, improve data management, reduce the cost of operations, and enhance better care for patients through more accessible and collaborative platforms.
These are the enlarging volume of health care data, pressure from cost, the need for better access, and the growing demand for remote and telemedicine services.
Cloud computing enhances business value to healthcare organizations in the following ways: efficiency improvement, allowance of innovation, reduction in IT costs, and improvement in patient care through faster data-driven decision-making processes.

Digital Valley, 423, Apple Square, beside Lajamni Chowk, Mota Varachha, Surat, Gujarat 394101
D-401, titanium city center, 100 feet anand nagar road, Ahmedabad-380015
+91 9913 808 2851133 Sampley Ln Leander, Texas, 78641
52 Godalming Avenue, wallington, London - SM6 8NW