Finance & IT Email Marketing: A Data-Driven Approach
February 2, 2026
Home >> Software >> Agile vs Traditional Project Management: Which One Is Right?

The process of planning, communicating, organizing, adapting, and managing resources is known as project management.
It entails determining and balancing the scope, time, cost, quality, and resources of the project. Agile project management and conventional project management are two distinct methods to project management.
In both Agile Management and traditional management, the project manager manages and monitors the project.
They make decisions to keep the project on track and on schedule to accomplish its objectives. Risk management, quality management, and change management are all required in both methods.
With that stated, let us examine the differences between Agile and Traditional Project Management, as well as the similarities, and how Agile vs Traditional Project Management compare.
Agile Certification might also be beneficial to you. Taking this course will help you improve your Agile learning.
As the name implies, project management employs specific knowledge, skills, tools, and strategies to provide something of value to people.
Simply simply, it entails supervising all of the activities, resources, and objectives required to finish a project.
Work is planned and organized, deadlines are set, progress is tracked, and stakeholder communication is kept up to date.
Project management allows for more efficient resource utilization, ensures project deadlines are met, and assists teams in organizing and focussing their goals in the most effective methods possible.
The classic Project Management (waterfall) technique is linear, with all steps of a project occurring in chronological order.
Its concept is based on reliable tools and experience. As illustrated in the graphic above, each project goes through the same life cycle, which comprises stages like feasibility, planning, designing, constructing, testing, production, and support.
Agile project management focuses on cooperation, communication, timeboxing, and the ability to quickly adapt to change.
There is an emphasis on flexibility, working together as a team, and involving the customer in the process. Customer input is taken into consideration and progress is made in regular intervals.
This iterative strategy takes into account user feedback and regular releases.
The core principle of agile project management is that it uses adaptation and collaboration to create better outcomes than a preset approach, highlighting the difference between traditional project management and agile project management.
| Aspect | Agile Project Management | Traditional Project Management |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Adaptive and flexible | Predictive and structured |
| Project Requirements | Customer collaboration and working software are prioritize | Comprehensive project requirements are defined upfront |
| Change Management | Welcomes changes during the project | Changes are discouraged or require formal approval |
| Communication | Emphasizes face-to-face communication and collaboration | Relies on formal written documentation |
| Project Planning | Short, iterative planning with room for adjustments | Long-term, detailed planning with limited flexibility |
| Team Structure | Cross-functional and self-organizing teams | Functionally divided teams with hierarchical structure |
| Organizational Structure | Flexible and adaptable organizational structure | Rigid and hierarchical organizational structure |
| Project Scale | Suitable for smaller to medium-sized projects | Suitable for larger and complex projects |
| Development Model | Iterative and incremental development | Linear and sequential development |
| User Involvement | High user involvement and feedback throughout | Limited user involvement until project completion |
| Client Collaboration | Collaborative and continuous client involvement | Client involvement at specific project milestones |
| Risk Management | Embraces uncertainty and adapts to changing risks | Risk assessment and mitigation planning are performed upfront |
| Documentation | Lean documentation with a focus on working solution | Comprehensive documentation for planning and compliance |
| Delivery Frequency | Frequent, incremental deliveries | Single, final delivery at project completion |
| Quality Assurance | Ongoing testing and quality assurance throughout | Testing typically conducted at the end of the project |
| Customer Satisfaction | High emphasis on customer satisfaction and feedback | Meeting predefined project objectives is the priority |
| Project Control | Self-monitoring and self-control by the project t | Centralized control and monitoring by project managers |
| Scope Changes | Welcomes scope changes even late in the project | Scope changes are discouraged and may lead to delays |
| Project Success Measurement | Frequent deliveries and customer satisfaction | Adherence to the original plan and meeting predefined criteria |
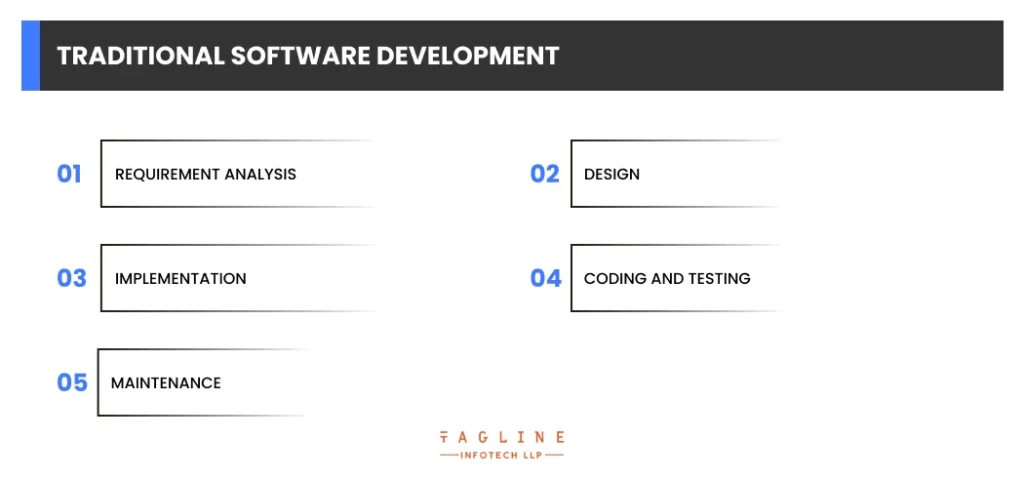
Traditional software development is the process of designing and developing basic software, often associated with traditional project management vs agile project management. It is used when the security and other aspects of the program are unimportant and is typically employed by newcomers to construct software. It is divided into five stages:
This phase entails gathering and documenting all project needs, which is usually done in the form of a detailed requirements specification document.
Based on the requirements obtained, the system architecture and design are designed and documented at this phase.
During this phase, the actual coding and development of the programme takes place in accordance with the design specifications.
Developers build the code, which is subsequently rigorously tested to discover and correct any errors or issues.
Following deployment, continued maintenance is necessary to resolve any issues, add new features, or upgrade the programme as needed during its existence.
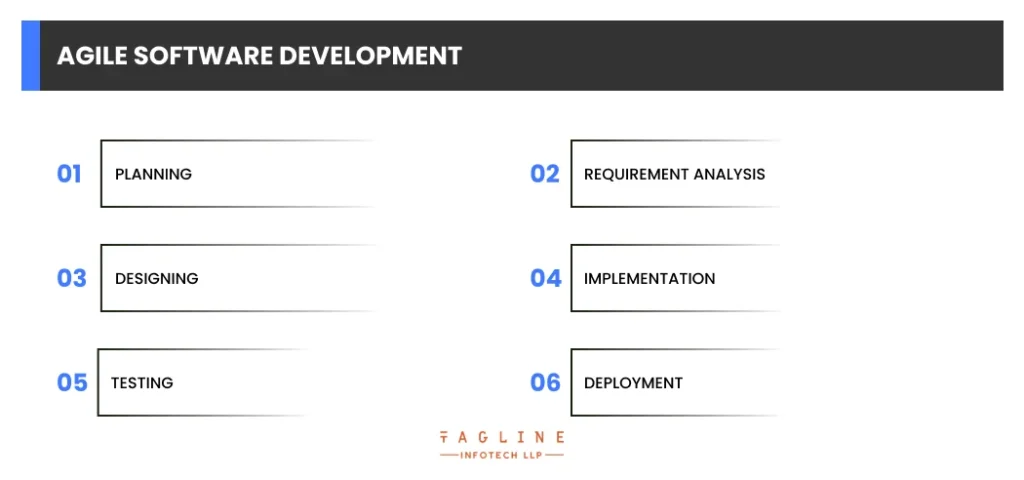
Agile Software Development is a software development technique that is used to create complex applications, highlighting the differences in traditional project management vs agile methodology. It is utilized when the program is extremely sensitive and complex, and when security is of the utmost importance. It is used by programmers to create software and is divided into six stages:
Agile initiatives begin with high-level planning to identify the general scope, goals, and objectives of the project.
Agile requires continuous and iterative requirement analysis. Throughout the project, requirements are collected sequentially.
Agile projects often feature lightweight design conversations and tweaks as the project advances, rather than a complete design phase.
Development proceeds in stages based on current requirements and design decisions.
Continuous testing is carried out throughout the development process, with each iteration properly tested.
Agile projects frequently deliver smaller software increments to users as soon as they are available, allowing for faster feedback and user interaction.
Ready to Embrace Agile Project Management for Enhanced Flexibility and Efficiency?
Hire our skilled team and experience the power of Agile over Traditional Project Management and unleash the potential of your projects
Also Read : Boosting Productivity and Innovation with 10 Software Development
You must have a clear idea of the benefits and drawbacks of both traditional versus agile project management by now, right? So you must realize that the decision between the two processes is dependent on the individual demands and limits of a project, particularly when it comes to effective product creation and management.
Agile project management is useful for projects with a lot of uncertainty or changing demands.
The conventional technique is suited for projects with stable or well-defined circumstances where no adjustments are required.
Furthermore, consider the project restrictions, such as the budget, timeframe, and resources, since this will assist you determine which model to use. In certain cases, the project team will choose a hybrid strategy that combines elements of agile and traditional project management to assist you achieve a balance between predictability and flexibility.
In the dynamic global of assignment management, the selection among Agile and Traditional methodologies isn’t always one-length-fits-all.
Each method gives wonderful advantages and drawbacks, making them suitable for unique varieties of projects. You should find a Hire Software Developer who can deliver amazing software for your business. To summarize:
Agile Project Management emphasizes adaptability, commonplace conversation, and customer collaboration. It’s excellent for projects with evolving requirements and a want for quick iterations.
Traditional Project Management, additionally called the Waterfall technique, follows a based, sequential procedure with properly described stages. It’s suitable for initiatives with solid requirements and a focal point for distinct planning.
The decision for traditional project management vs agile should be based totally on the precise traits and constraints of your challenge so choose wisely Agile vs Traditional Project Management
In some instances, a hybrid method that mixes elements of each methodology can be the handiest way to stability predictability, and versatility.
Yes, it is possible to apply a hybrid approach that mixes elements of both methodologies, known as "Agile-Waterfall Hybrid" or "Water-Scrum-Fall." This can offer a balance between structure and adaptability.
Agile may be faster in delivering incremental results and adapting to modifications, at the same time as Traditional can also have longer making plans levels. However, the general timeline depends on the venture's complexity and requirements.

Digital Valley, 423, Apple Square, beside Lajamni Chowk, Mota Varachha, Surat, Gujarat 394101
D-401, titanium city center, 100 feet anand nagar road, Ahmedabad-380015
+91 9913 808 2851133 Sampley Ln Leander, Texas, 78641
52 Godalming Avenue, wallington, London - SM6 8NW